80-82 Cao Duc Lan, District 2, HCMC, Vietnam
+84 76 865 6688
info@beetech.com.vn
+84 76 865 6688
About us
Contact us
80-82 Cao Duc Lan, District 2, HCMC, Vietnam
+84 76 865 6688
info@beetech.com.vn
+84 76 865 6688
About us
Contact us

Barcode Not Scanning? 7 Common Reasons and Effective Solutions
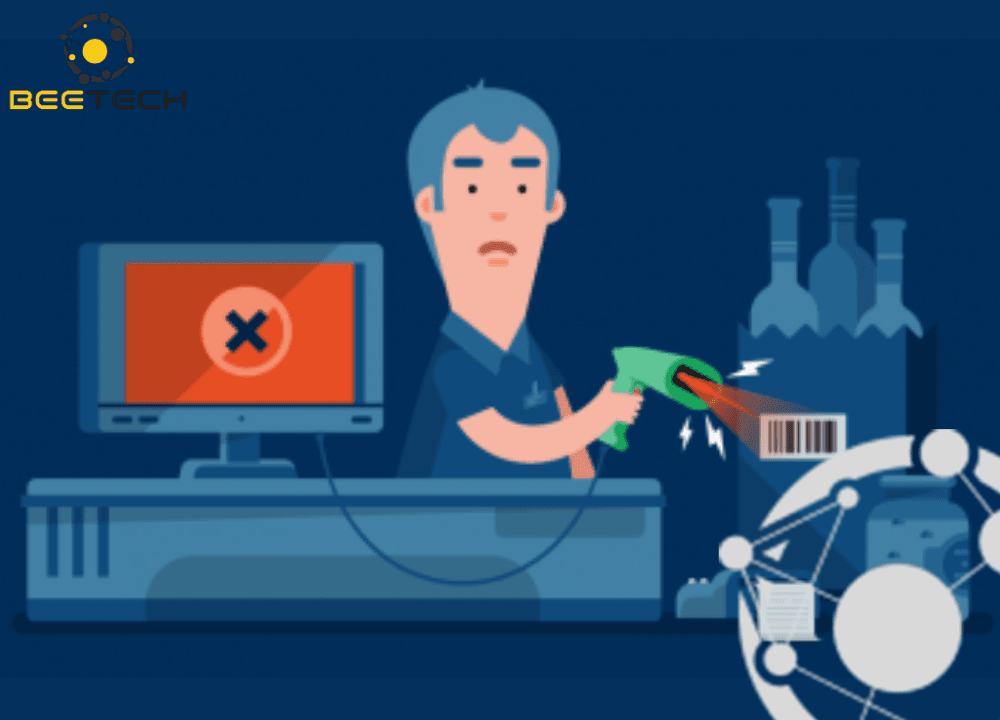
In the era of digitalization and automation, barcodes have become an indispensable tool in most processes involving inventory management, retail, logistics, and warehousing. However, a seemingly small issue that can significantly impact operational efficiency is: barcode scanners fail to read barcodes.
When barcodes are unreadable, it may lead to delays in order processing, inventory discrepancies, increased operational costs, and even a loss of customer trust. This article outlines the 7 most common reasons barcodes fail to scan and provides detailed solutions for each situation.
Below are the 7 most frequent barcode-related errors companies face.
Causes:
Low ink levels, poor-quality ink, or incompatible ink types.
Dirty print heads causing unclear lines.
Printing on uneven or moist surfaces, leading to smudging.
Consequences:
The barcode lacks sufficient contrast for the scanner to detect.
Some bars may appear broken or too light.
Solutions:
Use genuine label paper and ink.
Clean the print head regularly.
Ensure your printer has a resolution of at least 300dpi.
Adjust barcode printing settings (darkness, speed) in your software.
Causes:
Incorrect barcode scaling to save space on labels.
The barcode is stretched or compressed unevenly.
Consequences:
Small barcodes cause lines to merge—scanners can’t distinguish them.
Oversized barcodes may not fit within the scanner’s field of view.
Solutions:
Maintain a minimum bar width of 0.3mm.
Preserve the correct aspect ratio when resizing.
Use professional software like Bartender or NiceLabel to ensure standard-compliant output.
Causes:
Printed on glossy paper, metal, reflective surfaces, or transparent plastic.
No white background layer beneath the barcode.
Consequences:
Scanner light reflects off the surface, distorting the signal.
Laser or CCD scanners struggle to distinguish light/dark zones.
Solutions:
Always print on white matte paper or non-reflective labels.
For special materials (e.g., glass, metal), use laser-engraved barcodes or add a printed white background.
Consider RFID or 2D camera scanners for reflective surfaces.
Causes:
Input errors such as missing check digits or invalid characters.
Using a format unsupported by the scanner.
Using non-standard barcode fonts.
Consequences:
Scanner may detect the barcode but return incorrect or blank data.
Barcode becomes completely unreadable.
Solutions:
Verify the barcode format: QR Code, Code 39, Code 128, EAN-13, UPC, etc.
Use reputable barcode generation software (e.g., Zint, Barcode Generator, iBarcoder).
Ensure your scanner supports the specific format in use.
Causes:
Barcodes placed in high-friction areas, leading to scratches or tears.
Applied on soft or curved packaging that distorts the code.
Consequences:
Missing lines or partial damage prevents decoding.
Scanning errors or failures.
Solutions:
Apply barcodes on flat, clean, and secure areas.
Use laminated or coated labels for protection in harsh environments.
Regularly inspect barcode labels for damage.
Causes:
Holding the scanner too close or too far from the barcode.
Tilting the scanner or holding it at an improper angle.
Consequences:
Weak signal or failed scan.
Delayed reading speed or complete inoperability.
Solutions:
Position the scanner at 10–30cm from the barcode (depending on scanner specs).
Keep the scanner perpendicular to the barcode surface.
Use scanners with a wide reading angle or 2D camera scanners for larger or oddly shaped barcodes.
Causes:
Dust or smudges on the scanning lens.
Low battery in wireless devices.
USB or Bluetooth connection interruptions.
Incorrect scanner settings (e.g., disabled barcode types).
Consequences:
All barcodes fail to scan.
Output may return errors or unreadable characters.
Solutions:
Clean the scanner sensor and lens.
Fully charge or replace batteries as needed.
Reconnect or reset the scanner.
Refer to the device manual to enable the appropriate barcode types.
Barcodes on both sides of a product may confuse scanners.
Overlapping or stacked barcodes cause signal confusion.
Poor lighting conditions (too bright or too dim) can affect scan accuracy.
Unreadable barcodes are not always the scanner’s fault—they can result from poor printing quality, improper placement, incorrect formatting, or user error. To ensure smooth workflow and scanning reliability:
✅ Use the right scanner type (Laser, CCD, 2D…)
✅ Generate and print barcodes with professional software
✅ Apply and store labels carefully
✅ Regularly maintain your scanning equipment
Contact Beetech for expert solutions in barcode systems, RFID, and warehouse automation:
🌐 Website: www.beetech.com.vn
📩 Email: info@beetech.com.vn



Barcode Technology in the Digital Age: Types, Advantages, Limitations, and How Businesses Can Choose the Right One
18/11/2025 04:12:49

5 Barcode Secrets That Smart Businesses in Vietnam Are Using to Boost Logistics Efficiency
12/11/2025 08:00:46

GS1 US adopts 2D barcodes and intelligent data capture – Advancing toward a transparent and modern supply chain
07/11/2025 06:33:27
Barcode Technology: The Classic Tool Evolving for a Digital Supply Chain Era
06/11/2025 03:37:29

Barcode – An efficient and cost-effective asset management solution for modern businesses
05/11/2025 04:20:46
The future of barcode scanning technology: Key trends and practical applications in the digital era
31/10/2025 04:21:05